Retirement Accounts and Their Importance
Retirement accounts play a crucial role in securing financial stability during our golden years. As we work towards building a comfortable future, understanding the importance of retirement savings and the various options available is essential.
Retirement accounts are specifically designed to help individuals save for their retirement. These accounts offer tax advantages and investment opportunities that can help grow your savings over time. By contributing to a retirement account, you are setting aside funds that will support you when you decide to stop working.
Saving for retirement is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures that you have enough income to maintain your desired lifestyle after leaving the workforce. With rising life expectancies and increasing healthcare costs, having sufficient savings becomes even more critical.
Additionally, starting early and consistently contributing to a retirement account allows your investments to benefit from compounding interest. This means that over time, your money can grow exponentially through the power of reinvesting earnings.
Furthermore, relying solely on government benefits or pensions may not be sufficient to meet all your financial needs during retirement. Having personal savings in a dedicated retirement account provides an additional layer of security and peace of mind.
Understanding the importance of retirement savings and utilizing retirement accounts as part of your overall financial planning strategy is vital for a secure future. By taking advantage of these accounts and starting early, you can build a nest egg that will support you throughout your retired years.
Table of Contents
The Different Types of Retirement Accounts
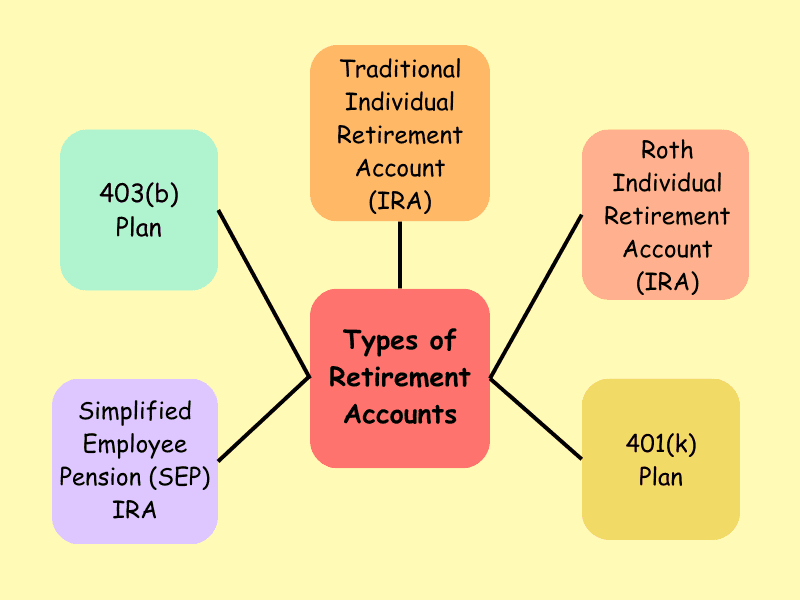
Traditional Individual Retirement Account (IRA)
A traditional Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is a popular retirement savings option that offers tax advantages to individuals. With a traditional IRA, contributions are made on a pre-tax basis, meaning that the money you contribute is deducted from your taxable income for the year. This can result in immediate tax savings.
One of the key benefits of a traditional IRA is that contributions grow on a tax-deferred basis. This means that you won’t have to pay taxes on any investment gains or earnings within the account until you make withdrawals in retirement.
Eligibility criteria for contributing to a traditional IRA include having earned income and being under the age of 70½. There are also income limits for individuals who have access to an employer-sponsored retirement plan such as a 401(k) or 403(b). However, even if you exceed these limits, it may still be possible to contribute to a traditional IRA through what is known as a “backdoor” Roth conversion.
When it comes to withdrawing funds from a traditional IRA, there are rules and considerations to keep in mind. Withdrawals made before age 59½ may be subject to an early withdrawal penalty of 10% in addition to ordinary income taxes. However, there are certain exceptions such as using funds for qualified higher education expenses or purchasing your first home.
Once you reach age 70½, you will need to start taking required minimum distributions (RMDs) from your traditional IRA each year. Failure to take these distributions can result in significant penalties.
Overall, a traditional IRA can be an effective tool for saving for retirement and enjoying potential tax advantages along the way. It’s important to understand the eligibility criteria and withdrawal rules associated with this type of account in order to make informed decisions about your retirement savings strategy.
Roth Individual Retirement Account (IRA)
A Roth Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is a type of retirement savings account that offers unique benefits to individuals looking to save for their future. Unlike a traditional IRA, contributions made to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax dollars, meaning that taxes have already been paid on the money before it is contributed.
One of the key advantages of a Roth IRA is that withdrawals in retirement are typically tax-free. This means that any earnings and growth within the account can be withdrawn without incurring additional taxes, as long as certain conditions are met. This can be highly beneficial for individuals who anticipate being in a higher tax bracket during retirement or who want to minimize their tax liability in the future.
It’s important to note that there are income limits associated with contributing to a Roth IRA. For 2021, single filers with modified adjusted gross incomes (MAGI) above $140,000 and married couples filing jointly with MAGIs above $208,000 may not be eligible to make direct contributions to a Roth IRA. However, there are strategies such as backdoor Roth conversions available for those who exceed these income limits but still want to take advantage of the benefits offered by a Roth IRA.
Overall, a Roth IRA provides individuals with an opportunity to save for retirement while enjoying potential tax-free growth and withdrawals. It’s worth considering this type of retirement account if you meet the eligibility criteria and want to maximize your tax advantages in the long run.
401(k) Plan
The 401(k) plan is an employer-sponsored retirement plan that allows employees to save and invest for their future. It has become a popular option for retirement savings due to its tax advantages and potential for employer matching contributions.
One of the key benefits of a 401(k) plan is the opportunity for employees to contribute pre-tax dollars from their paycheck, reducing their taxable income. This means that the money contributed to the plan grows tax-deferred until it is withdrawn during retirement.
However, it’s important to note that there are contribution limits set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). As of 2021, employees can contribute up to $19,500 per year to their 401(k) plan. Additionally, individuals who are age 50 or older can make catch-up contributions of up to an additional $6,500 per year.
Another advantage of a 401(k) plan is the potential for employer matching contributions. Many employers offer a match on employee contributions up to a certain percentage or dollar amount. This essentially provides free money towards an employee’s retirement savings.
In summary, a 401(k) plan is an employer-sponsored retirement savings vehicle that offers tax advantages and potential employer matching contributions. It allows individuals to save and invest for their future while taking advantage of pre-tax contributions and potential growth over time.
Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA
The Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA is a retirement savings plan designed specifically for self-employed individuals and small business owners. It offers several advantages and features that make it an attractive option for those looking to save for their future.
One of the key benefits of a SEP IRA is its high contribution limits. Unlike traditional IRAs or Roth IRAs, which have relatively low annual contribution limits, SEP IRAs allow self-employed individuals and small business owners to contribute a larger percentage of their income. In fact, the maximum contribution limit for a SEP IRA is significantly higher than that of other retirement plans, such as 401(k)s or SIMPLE IRAs.
This high contribution limit can be particularly advantageous for individuals with fluctuating incomes or those who want to save a substantial amount towards their retirement. It allows them to make larger contributions during years when their income is higher, helping them build up their retirement savings more quickly.
In addition to the high contribution limits, SEP IRAs also offer flexibility in terms of eligibility and administration. Self-employed individuals and small business owners can establish SEP IRAs even if they have no employees or choose not to cover them in the plan. This makes it an attractive option for sole proprietors or freelancers who want to save for retirement on their own terms.
Overall, the Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA provides self-employed individuals and small business owners with an effective tool to save for retirement while enjoying the benefits of high contribution limits and flexibility in plan administration.
403(b) Plan
The 403(b) plan is a retirement savings plan designed specifically for employees of non-profit organizations and public schools. Similar to the 401(k) plan for private sector employees, the 403(b) plan allows individuals to save and invest money for their retirement.
One key feature of the 403(b) plan is its contribution limits. As of 2021, the maximum amount an individual can contribute to their 403(b) account is $19,500. However, individuals who are age 50 or older can make additional catch-up contributions of up to $6,500, bringing their total contribution limit to $26,000.
It’s important to note that these contribution limits are subject to change each year based on inflation adjustments set by the IRS. It’s advisable for individuals participating in a 403(b) plan to stay updated on any changes in contribution limits.
The purpose of these contribution limits is to ensure that individuals have a fair opportunity to save for retirement while also maintaining tax advantages associated with these plans. By setting maximum amounts, it helps prevent high-income earners from disproportionately benefiting from the tax advantages offered by the 403(b) plan.
Overall, the 403(b) plan provides a valuable retirement savings option for employees of non-profit organizations and public schools. It allows them to contribute towards their future financial security while taking advantage of tax benefits provided by this specific type of retirement savings account.
Differences Between These Retirement Accounts and Which One is Right for You?
When it comes to planning for retirement, understanding the differences between various retirement accounts is crucial. Two commonly compared options are the traditional IRA and Roth IRA, each with its own set of advantages and considerations. Additionally, individuals may also need to weigh the differences between a 401(k) and SEP IRA if they are self-employed or have their own business.
The main distinction between a traditional IRA and a Roth IRA lies in how taxes are handled. Contributions to a traditional IRA are typically tax-deductible, but withdrawals during retirement are subject to income tax. On the other hand, contributions to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax dollars, meaning they are not tax-deductible at the time of contribution. However, qualified withdrawals from a Roth IRA during retirement can be tax-free.
For those who have access to an employer-sponsored plan such as a 401(k), it’s important to understand how it differs from an SEP (Simplified Employee Pension) IRA. A 401(k) is offered by employers and allows employees to contribute pre-tax dollars directly from their paycheck. Employers may also provide matching contributions up to a certain percentage. In contrast, an SEP IRA is designed for self-employed individuals or small business owners who want to save for retirement while enjoying potential tax benefits.
When choosing the right retirement account based on employment status, several factors should be considered. For employees with access to an employer-sponsored plan like a 401(k), it’s often wise to take advantage of any employer matching contributions before exploring other options. Self-employed individuals or small business owners may find that an SEP IRA offers more flexibility in terms of contribution limits and potential tax deductions.
Ultimately, selecting the most suitable retirement account depends on individual circumstances such as income level, current tax situation, future financial goals, and personal preferences regarding taxation during retirement. Consulting with a financial advisor can provide valuable insights tailored specifically to one’s unique situation and help make informed decisions about retirement planning.
The Benefits of Diversifying Your Retirement Savings Across Multiple Accounts
Diversifying your retirement savings across multiple accounts can offer several benefits. By employing diversification strategies, you can mitigate risk and potentially maximize your investment growth. In this section, we will explore the advantages of diversifying your retirement savings and the various ways you can achieve this.
One key benefit of diversification is reducing the impact of market volatility on your overall portfolio. By spreading your investments across different accounts, such as individual retirement accounts (IRAs), 401(k)s, or brokerage accounts, you can minimize the potential impact of a downturn in a particular asset class or sector.
Another advantage is taking advantage of tax benefits. Different types of retirement accounts offer various tax advantages that can help optimize your savings strategy. For example, traditional IRAs and 401(k)s provide tax-deferred growth, allowing you to potentially reduce your taxable income during your working years. On the other hand, Roth IRAs offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
Furthermore, diversifying investments across multiple accounts allows for greater flexibility in managing and accessing funds during retirement. Having a mix of taxable and tax-advantaged accounts provides options for withdrawing money based on your specific financial needs while potentially minimizing taxes.
Maximizing investment growth through diversification is another crucial aspect to consider. Allocating assets across different types of investments like stocks, bonds, real estate investment trusts (REITs), or mutual funds can help spread risk while potentially capturing higher returns over time.
In conclusion, diversifying your retirement savings across multiple accounts offers several benefits including risk mitigation, tax advantages, flexibility in accessing funds during retirement, and potential for maximizing investment growth. By exploring different account options and employing effective diversification strategies tailored to your financial goals and risk tolerance level, you can enhance the long-term success of your retirement plan.
Securing Your Future with the Right Retirement Account
Planning for retirement is a crucial step in securing your financial future. One of the key components of a successful retirement strategy is choosing the right retirement account. By understanding the different options available and selecting the one that aligns with your goals and needs, you can ensure a comfortable and stress-free retirement.
There are several types of retirement accounts to consider, such as 401(k)s, individual retirement accounts (IRAs), Roth IRAs, and pension plans. Each has its own set of features, benefits, and eligibility requirements. It’s important to evaluate these factors carefully before making a decision.
A 401(k) is an employer-sponsored plan that allows employees to contribute a portion of their salary towards their retirement savings on a pre-tax basis. This type of account often comes with employer matching contributions, providing an additional boost to your savings.
On the other hand, IRAs are individual accounts that offer tax advantages for individuals who do not have access to an employer-sponsored plan or want more control over their investment choices. Traditional IRAs allow for tax-deductible contributions, while Roth IRAs offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
Pension plans are another option for securing your future income during retirement. These plans are typically offered by employers and provide guaranteed income based on factors such as years of service and salary history.
When choosing the right retirement account for you, consider factors such as your current income level, expected future income needs, desired level of control over investments, and tax implications. Consulting with a financial advisor can help you navigate these decisions and create a personalized plan tailored to your unique circumstances.
Remember that it’s never too early or too late to start saving for retirement. The sooner you begin contributing to a retirement account and taking advantage of any employer matching contributions available to you, the more time your money will have to grow through compounding interest.
Securing your future with the right retirement account is essential for a comfortable and financially stable retirement. Take the time to educate yourself about the various options available, seek professional advice if needed, and start saving as early as possible. By making informed decisions and consistently contributing to your retirement account, you can enjoy a worry-free retirement filled with peace of mind.


1 thought on “Understanding the Different Types of Retirement Accounts: A Comprehensive Guide”